307.Range Sum Query - Mutable
Given an integer array nums, find the sum of the elements between indices i and j (i≤j), inclusive. The update(i, val) function modifies nums by updating the element at index i to val.
Example:
Given nums = [1, 3, 5]
sumRange(0, 2) -> 9
update(1, 2)
sumRange(0, 2) ->8
Note:
- The array is only modifiable by the update function.
- You may assume the number of calls to update and sumRange function is distributed evenly.
S: binary index tree O(logn)
BIT tree store the sum of certain numbers of elements, get the sum of 0 - j by add up BIT[j] and all its ancestors.
When update an element, need to update BIT[j] and all its descendants
class NumArray {
public:
NumArray(vector<int> nums) {
myNum = nums;
size = nums.size();
BIT = vector<int>(size + 1, 0); //BIT need one more space, root node is a dummy node
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
add(i + 1, nums[i]); //BIT index is one more than the original index
}
}
void update(int i, int val) {
int diff = val - myNum[i];
myNum[i] = val;
add(i + 1, diff);
}
int sumRange(int i, int j) {
return getSum(j + 1) - getSum(i);
}
private:
vector<int> myNum;
vector<int> BIT;
int size;
void add(int i, int val) {
while (i <= size) { //BIT's size is size+1 so we use <= here
BIT[i] += val; //add value to all i's descendants
i += (i & -i); //get child index
}
}
int getSum(int i) {
int sum = 0;
while (i > 0) {
sum += BIT[i]; //add all i's ancestor's value to sum
i -= (i & -i); //get parent index
}
return sum;
}
};
308. Range Sum Query 2D - Mutable
Given a 2D matrix matrix, find the sum of the elements inside the rectangle defined by its upper left corner (row1, col1) and lower right corner (row2, col2).
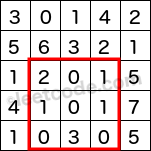
The above rectangle (with the red border) is defined by (row1, col1) = (2, 1) and (row2, col2) = (4, 3), which contains sum = 8.
Example:
Given matrix = [
[3, 0, 1, 4, 2],
[5, 6, 3, 2, 1],
[1, 2, 0, 1, 5],
[4, 1, 0, 1, 7],
[1, 0, 3, 0, 5]
]
sumRegion(2, 1, 4, 3) -> 8
update(3, 2, 2)
sumRegion(2, 1, 4, 3) -> 10
Note:
- The matrix is only modifiable by the update function.
- You may assume the number of calls to update and sumRegion function is distributed evenly.
- You may assume that row1 ≤ row2 and col1 ≤ col2.
S: Binary index tree (logm * logn)
二维BIT, 对于每一行进行一维BIT处理
class NumMatrix {
public:
NumMatrix(vector<vector<int>> matrix) {
nums = matrix;
row = matrix.size();
if (row > 0) col = matrix[0].size();
BIT = vector<vector<int>>(row + 1, vector<int>(col + 1, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; ++j) {
add(i + 1, j + 1, matrix[i][j]);
}
}
}
void update(int r, int c, int val) {
int diff = val - nums[r][c];
add(r + 1, c + 1, diff);
nums[r][c] = val;
}
int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
int sum_rightbot = getSum(row2 + 1, col2 + 1);
int sum_righttop = getSum(row1, col2 + 1);
int sum_leftbot = getSum(row2 + 1, col1);
int sum_lefttop = getSum(row1, col1);
return sum_rightbot - sum_righttop - sum_leftbot + sum_lefttop;
}
private:
vector<vector<int>> nums;
vector<vector<int>> BIT;
int col = 0;
int row = 0;
void add(int i, int j, int val) {
for (; i <= row; i += i & -i) {
//start at j for each row
for (int colId = j; colId <= col; colId += colId & -colId) {
BIT[i][colId] += val;
}
}
}
int getSum(int i, int j) {
int sum = 0;
for (; i > 0; i -= i & -i) {
for (int colId = j; colId > 0; colId -= colId & -colId) {
sum += BIT[i][colId];
}
}
return sum;
}
};